¶ Introduction
The POST /ligand-detection endpoint allows you to correct ligand information for an existing structure without re-uploading it. This ensures accurate chemical representation and improves searchability in 3decision.
Details on how the endpoint works can be found at this page of the User Guide.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use this endpoint to fix ligand errors efficiently.
¶ Tutorial
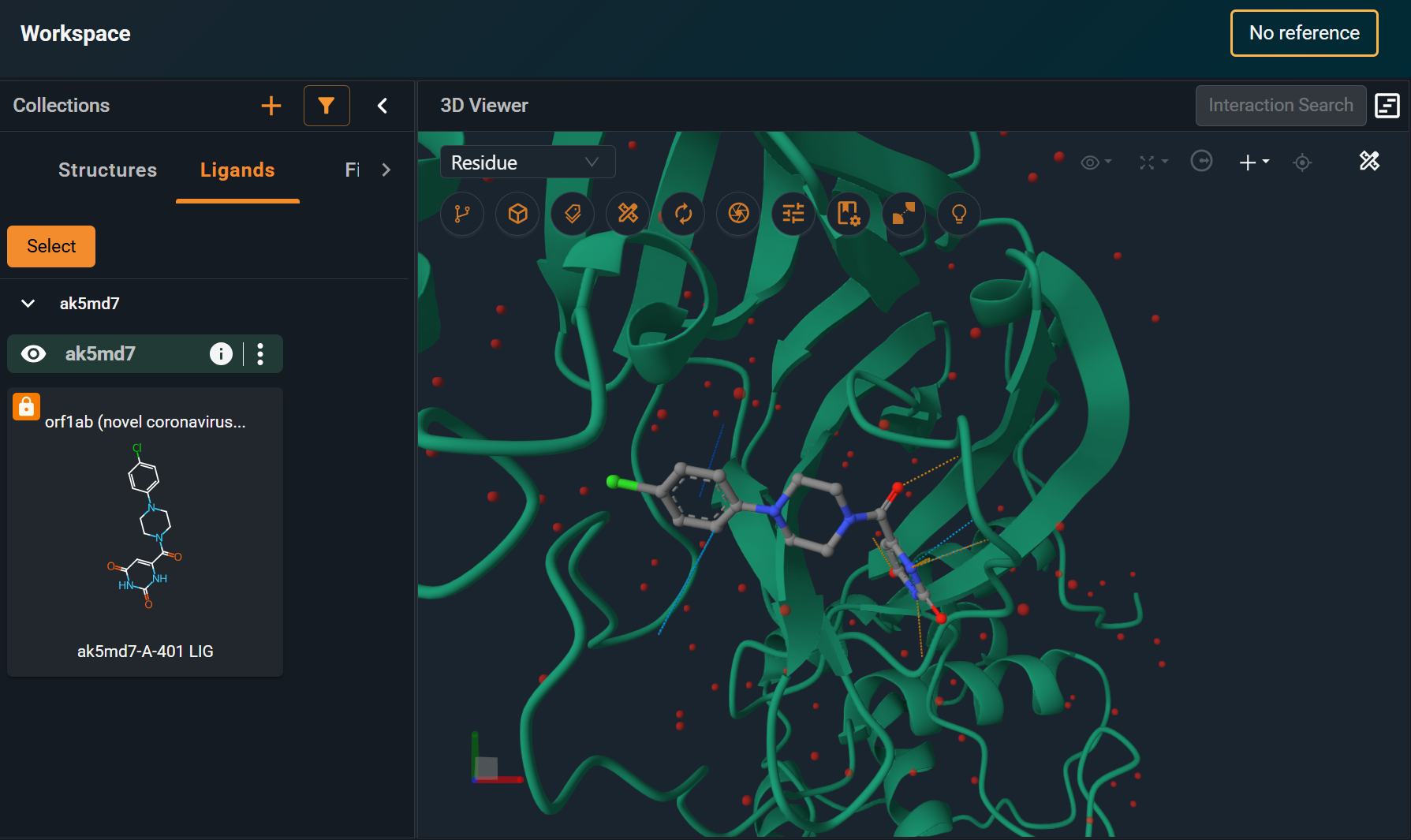
In this tutorial, we'll work on a 3decision structure entry with an incorrectly registered ligand. The aim of the tutorial is to fix this error using the POST /ligand-detection endpoint.
As an example, you can see in the screenshot that when opening the registered structure in the Workspace, the 2D representation of the ligand is missing the double bonds. In the section below, we will see how to fix this.
¶ 1. Access the 3decision API Documentation (Swagger API page)
- Log in to the 3decision user interface
- Click on the "My Profile" icon (bottom left) and select "API"
- Click on "3decision API Endpoint Definition" (link at the top)
If you want to run these API calls through a Python script (or something similar), you'll find instructions on how to authenticate here.
¶ 2. Submit a Detection Job
To launch the ligand detection analysis, you need to use the API endpoint: POST /ligand-detection.
¶ Parameters
externalCode: The structure external codetemplates: Array of ligand template objects defining the correct chemical structure. Each template requires:residueCode: Three-letter ligand identifier from your structure (e.g., "LIG", "ATP")smiles: SMILES string representing the correct molecular structure with proper bond ordersinternalId: Internal compound database identifier (leave empty "" if not applicable)
matchAndCorrect: Selective correction mode - Whentrue, only corrects ligands that match your provided templates, leaving unmatched ligands unchanged. Useful for targeted fixes in multi-ligand structures (default =false)strictMatch: Quality assurance flag - Whentrue, the operation fails if any provided template cannot be matched to a ligand in the structure, ensuring all expected corrections occur (default =false)commit: Database persistence control - Must betrueto permanently save changes to the database. Set tofalsefor validation runs without making actual modifications (default =false)
NB. If templates is left empty, the system automatically tries to correct the ligands in the strucure with templates from the Chemical Component Dictionary and MOE-based inference from coordinates.
¶ Example Request
{
"externalCode": "ak5md7",
"templates": [
{
"residueCode": "LIG",
"smiles": "Clc1ccc(cc1)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C3=CC(=O)NC(=O)N3",
"internalId": ""
}
],
"matchAndCorrect": true,
"strictMatch": true,
"commit": true
}
¶ Example curl Command
curl -X POST "https://api.3decision.com/ligand-detection" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-d '{
"externalCode": "ak5md7",
"templates": [
{
"residueCode": "LIG",
"smiles": "Clc1ccc(cc1)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C3=CC(=O)NC(=O)N3",
"internalId": ""
}
],
"matchAndCorrect": true,
"strictMatch": true,
"commit": true
}'
¶ 3. Check the Status of the Job
To check the status of the ligand detection analysis, you can use the API endpoint: GET /ligand-detection, using as an input the structure external code. If you get a "success" the analysis was successfully completed.
¶ Example Response
{
"state": "success",
"content": [
{
"small_mol_id": 144713,
"matching_template": "Clc1ccc(cc1)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C3=CC(=O)NC(=O)N3",
"residue_code": "LIG"
}
]
}
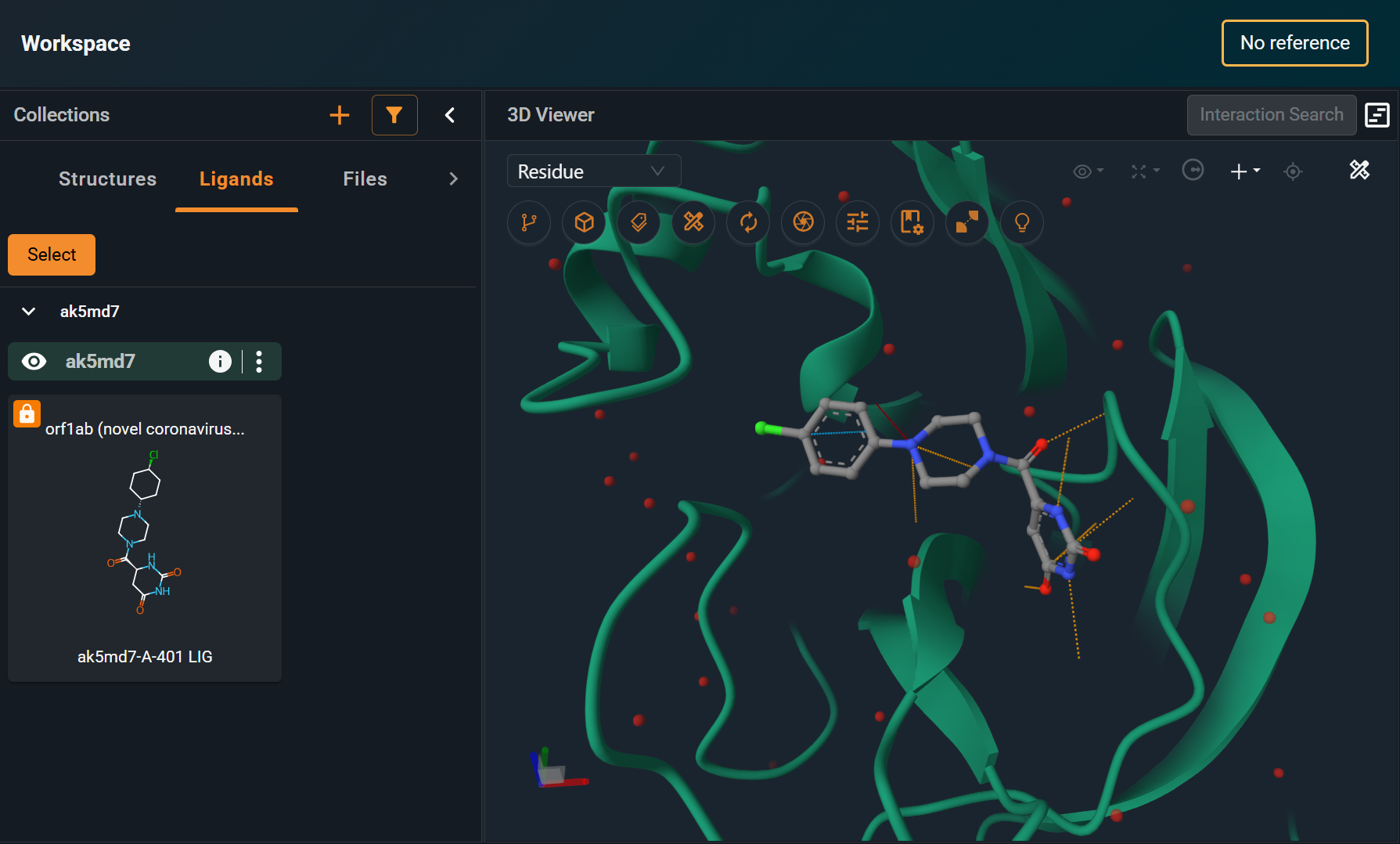
¶ 4. Check Ligand Was Corrected in the UI
Open the structure in the Workspace again, and ensure that the ligand is now displayed correctly. In this example, now the 2D representation matches the correct bond order displayed in 3D.